The road to Emancipation was indeed stony! Enslaved people struggled to free themselves and loved ones, one person at a time.
This activity includes primary sources from the official records of the U.S. District Court at Boston that tell the story of William and Ellen Craft, a young couple from Macon, GA, who escaped to freedom in Boston in 1848. The two traveled together, Ellen as a White gentleman (she was the daughter of an African-American woman and a White master and passed as White), and William as her slave valet. They made their way to Boston, and lived in the home of Lewis Hayden, a former fugitive and abolition activist.
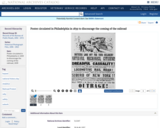
With the passing of the Fugitive Slave Act in September, 1850, the Crafts' respective owners employed the legal system to regain their escaped property. A U.S. Marshal was sent to the home of Lewis Hayden. Hayden refused to let the marshal in and threatened to ignite kegs of gunpowder; the Marshal left. Ellen and William fled to Britain, where they remained for 20 years. They eventually returned to the United States and settled back in Georgia.
In this activity, students will examine historic documents about these fugitives from slavery. Then, using the documents, they will construct historical narratives to tell their story. They can explore perspective and use standard elements of writing (plot, character, setting, conflict, impact). Thinking about essential questions/topics, they will begin their writing with a topic/opening sentence that sets out the main idea.