
Flower Gardens Task Template and Student Version of Task
- Subject:
- Algebra I & II
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Lesson Plan
- Provider:
- VDOE
- Author:
- VDOE
- Date Added:
- 10/07/2024

Flower Gardens Task Template and Student Version of Task

Factoring Polynomials Mathematics Instructional Plan

Formative Assessment - Factor Polynomials in One or Two Variables - Just in Time Quick Check, Teacher Notes, and Supporting Resources
Build rectangles of various sizes and relate multiplication to area. Discover new strategies for multiplying algebraic expressions. Use the game screen to test your multiplication and factoring skills!
With your mouse, drag data points and their error bars, and watch the best-fit polynomial curve update instantly. You choose the type of fit: linear, quadratic, cubic, or quartic. The reduced chi-square statistic shows you when the fit is good. Or you can try to find the best fit by manually adjusting fit parameters.
Learn about graphing polynomials. The shape of the curve changes as the constants are adjusted. View the curves for the individual terms (e.g. y=bx ) to see how they add to generate the polynomial curve.
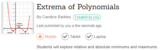
Students review domain, range, and intervals of increasing and decreasing using a draggable point to help them find extrema. Students find both absolute and relative extrema.

Just in Time Quick Check Operations on Polynomials

Just in Time Quick Check Operations on Polynomials

Just in Time Quick Check Operations on Polynomials including Factoring

A.2b Multiplying Polynomials Using Algebra Tiles Co-Teaching MIP

Students will use a draggable point to investigate intervals of increase and decrease and then practice writing and fining intervals.