
Rounding with Number Lines Algebra Readiness Remediation Plan
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Lesson Plan
- Provider:
- VDOE
- Author:
- VDOE
- Date Added:
- 10/07/2024

Rounding with Number Lines Algebra Readiness Remediation Plan
This lesson, which is a remix from an Illustrative Mathematics task, discusses the relation between multiplication and division. Fact families are also explored.https://goopenva.org/courses/3-oa-fish-tanks
This remixed lesson from Illustrative Mathematics models how to get the same sum with different addends. It is also introduces students to the use of number lines in addition. https://goopenva.org/courses/2-md-frog-and-toad-on-the-number-line

This resource is a remix from Illustrative Mathematics https://tasks.illustrativemathematics.org/content-standards/tasks/1081. Suggested Modifications: It is imperative that students in their early ages of mathematics education be introduced to the idea of the number line that makes sense. In other words, they usually count the tick marks on the number line which leads to an inaccuracy in the algorithm. To help them better understand number lines, the suggestion is to introduce the idea number paths which is another way of looking at a number line. To help better facilitate the lesson, I have added a downloadable document student activity that can be used in cooperative learning groups to facilitate mathematical discourse. This activity also encourages literacy in the curriculum.

In the first unit of Grade 3, students will build on their understanding of the structure of the place value system from Grade 2 (MP.7), start to use rounding as a way to estimate quantities (3.NBT.1), as well as develop fluency with the standard algorithm of addition and subtraction (3.NBT.2). Throughout the unit, students attend to the precision of their calculations (MP.6) and use them to solve real-world problems (MP.4).
In Grade 2, students developed an understanding of the structure of the base-ten system as based in repeated bundling in groups of 10. With this deepened understanding of the place value system, Grade 2 students “add and subtract within 1000, with composing and decomposing, and they understand and explain the reasoning of the processes they use” (NBT Progressions, p. 8). These processes and strategies include concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction (2.NBT.7). As such, at the end of Grade 2, students are able to add and subtract within 1,000 but often aren’t relying on the standard algorithm to solve.
Thus, Unit 1 starts off with reinforcing some of this place value understanding of thousands, hundreds, tens, and ones being made up of 10 of the unit to its right that students learned in Grade 2. Students use this sense of magnitude and the idea of benchmark numbers to first place numbers on number lines of various endpoints and intervals, and next use those number lines as a model to help students round two-digit numbers to the tens place as well as three-digit numbers to the hundreds and tens place (3.NBT.1). Next, students focus on developing their fluency with the addition and subtraction algorithms up to 1,000, making connections to the place value understandings and other models they learned in Grade 2 (3.NBT.2). Last, the unit culminates in a synthesis of all learning thus far in the unit, in which students solve one- and two-step word problems involving addition and subtraction and use rounding to assess the reasonableness of their answer (3.OA.8), connecting the NBT and OA domains. These skills are developed further and built upon in subsequent units in which multiplication and division are added to the types of word problems students estimate and solve.

In Unit 6, students extend and deepen Grade 1 work with understanding halves and fourths/quarters (1.G.3) as well as Grade 2 practice with equal shares of halves, thirds, and fourths (2.G.3) to understanding fractions as equal partitions of a whole. Their knowledge becomes more formal as they work with area models and the number line. Throughout the module, students have multiple experiences working with the Grade 3 specified fractional units of halves, thirds, fourths, sixths, and eighths. To build flexible thinking about fractions, students are exposed to additional fractional units such as fifths, ninths, and tenths.
This unit affords ample opportunity for students to engage with the Standards for Mathematical Practice. Students will develop an extensive toolbox of ways to model fractions, including area models, tape diagrams, and number lines (MP.5), choosing one model over another to represent a problem based on its inherent advantages and disadvantages. Students construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others as they explain why fractions are equivalent and justify their conclusions of a comparison with a visual fraction model (MP.3). They attend to precision as they come to more deeply understand what is meant by equal parts, and being sure to specify the whole when discussing equivalence and comparison (MP.6). Lastly, in the context of line plots, “measuring and recording data require attention to precision (MP.6)” (MD Progression, p. 3).
Unfortunately, “the topic of fractions is where students often give up trying to understand mathematics and instead resort to rules” (Van de Walle, p. 203). Thus, this unit places a strong emphasis on developing conceptual understanding of fractions, using the number line to represent fractions and to aid in students' understanding of fractions as numbers. With this strong foundation, students will operate on fractions in Grades 4 and 5 (4.NF.3—4, 5.NF.1—7) and apply this understanding in a variety of contexts, such as proportional reasoning in middle school and interpreting functions in high school, among many others.

This resource encourages literacy across the curriculum and the use of hands-on manipulatives to support and facilitate student understanding of the content. The illustrative mathematics incorporated a book and the suggested modifications will supplement the lesson allowing students to make relationship with the content and the real world. The suggested modification will allow students to have a mathematical discourse and use the language of mathematics.
Build equivalent fractions with different denominators. Match shapes and numbers to earn stars in the game. Challenge yourself on any level you like. Try to collect lots of stars!

Just in Time Quick Check Multistep Linear Equations on a Number Line
This video is part of the Continue to Know with WHRO TV series. Watch Emily Rathbone teach about multiplying decimals.

The original lesson plan that can be found https://tasks.illustrativemathematics.org/content-standards/tasks/371 started with an activity on comparing numbers on the number line. The suggested modification activity about the human number line will help students understand that large numbers move to the right of the number line and vice versa.
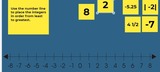
Place integers on the number line. Then write integers in order from greatest to least or least to greatest as requested. Use the number line to help make conceptual connections about positive and negative integers.

This video is part of the Continue to Know with WHRO TV series. Watch Kathryn Turner teach about representing integers using counters and number lines.