
A simple Python program to determine if two words are anagrams
- Subject:
- Algorithms and Programming
- Computer Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Assessment
- Homework/Assignment
- Author:
- Ronald Sparks
- Date Added:
- 05/25/2022

A simple Python program to determine if two words are anagrams

This activity will allow students to compare Brute Force and Divide and Conquer sorting algorithms.This activity will show the sorting process of a Brute Force algorithm and a Divide and Conquer algorithm that is used by a computer when sorting data.

This activity will show the sorting process using the Bubble Sort Brute Force algorithm that is used by a computer when sorting data without using a computer.

These modules are designed to help you get familiar with Python while exploring interactive narrative design, where we put together stories that leave space for the reader to explore, make choices, and engage with the events of the story in a participatory way. Each module in this course follows the same format:Backstory: Unpack the context around the module, set up catalyzing questions to guide the inquiry throughout the module, and establish goals and objectives for your engagement with the moduleGuided Inquiry: Step through a sequence of tutorials and hands-on activities designed to help you learn the basic ideas presented in the modulesPrompt: A tightly-bounded, focused activity designed to facilitate sustained engagement with the ideas presented in the moduleCatalyzing Questions: A series of questions intended to provoke reflection & to put the module’s content in contextEach module is intended to support between 30 and 60 minutes of focused, sustained engagement. You may find it suits you to leave the module in the middle and return to your work; that’s totally fine. Work at your own pace, and don’t hesitate to reach out to your facilitators if you run into any problems.

Suffolk Public Schools is the host of an annual robotics challenge sponsored by Penn State and the US Department of Defense. ActiVAtED Learning Host Tom Landon traveled to Suffolk to talk to Christine Lafferty and John Littlefield to learn more.

This is a lesson plan on iteration and looping to be used with high school aged students who are using the python programming language. This resource includes a PowerPoint presentation along with a python file for students to use to practice the concept of iteration. The python file has areas in which the student is asked to complete the statement by inserting variables in the program. As the student works through the steps of the program, the steps build up to the final task which is to write the code for a basic random number generator.

This activity will show the sorting process using the Merge Sort Divide and Conquer algorithm that is used by a computer when sorting data without using a computer.

In this lesson sequence, students will work in teams to learn the MakeCode and Micro:Bit Development platform. They’ll develop basic programming skills, implementing input, output, variables, and conditional control structures. At the end of the sequence, students will compete in a “puzzle box” challenge, attempting to create a puzzle using their Micro:Bit, code, and craft supplies and earning points based on how challenging their puzzle is to solve.

This activity will show the sorting process using the Quick Sort Divide and Conquer algorithm that is used by a computer when sorting data without using a computer.
A simple calculator in Python to add, subtract, multiply and divide

This lesson introduces 9-12 grade students to the tuple data type using Python. Students will learn what tuples are and how to create and use them.
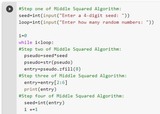
What is Random? Through this project, students will discover what makes an outcome random. Emphasis will be placed on the difference between deterministic and nondeterministic outcomes. The project starts out with a discovery activity where students will see the difference between creating data with a coin toss where they just make up the data and creating data through actually tossing a coin.Students will end the project by studying pseudorandom number generators, specifically the Middle Squared Algorithm. They will even create a program that uses this algorithm. Enjoy!