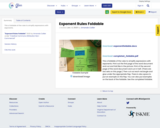
This a foldable of the rules to simplify expressions with exponents.
- Subject:
- Algebra I & II
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Lecture Notes
- Date Added:
- 12/30/2019

This a foldable of the rules to simplify expressions with exponents.

In this module, students draw on their foundation of the analogies between polynomial arithmetic and base-ten computation, focusing on properties of operations, particularly the distributive property. Students connect multiplication of polynomials with multiplication of multi-digit integers and division of polynomials with long division of integers. Students identify zeros of polynomials, including complex zeros of quadratic polynomials, and make connections between zeros of polynomials and solutions of polynomial equations. Students explore the role of factoring, as both an aid to the algebra and to the graphing of polynomials. Students continue to build upon the reasoning process of solving equations as they solve polynomial, rational, and radical equations, as well as linear and non-linear systems of equations. The module culminates with the fundamental theorem of algebra as the ultimate result in factoring. Students pursue connections to applications in prime numbers in encryption theory, Pythagorean triples, and modeling problems.
To access this resource, you will need to create a free account for the system on which it resides. The partner provides personalized features on their site such as bookmarking and highlighting which requires a user account.

In this module, students synthesize and generalize what they have learned about a variety of function families. They extend the domain of exponential functions to the entire real line and then extend their work with these functions to include solving exponential equations with logarithms. They use appropriate tools to explore the effects of transformations on graphs of exponential and logarithmic functions. They notice that the transformations of a graph of a logarithmic function relate to the logarithmic properties. Students identify appropriate types of functions to model a situation. They adjust parameters to improve the model, and they compare models by analyzing appropriateness of fit and making judgments about the domain over which a model is a good fit. The description of modeling as "the process of choosing and using mathematics and statistics to analyze empirical situations, to understand them better, and to make decisions" is at the heart of this module. In particular, through repeated opportunities in working through the modeling cycle, students acquire the insight that the same mathematical or statistical structure can sometimes model seemingly different situations.
To access this resource, you will need to create a free account for the system on which it resides. The partner provides personalized features on their site such as bookmarking and highlighting which requires a user account.

By the end of Grade 8, students have learned to solve linear equations in one variable and have applied graphical and algebraic methods to analyze and solve systems of linear equations in two variables. Now, students are introduced to nonlinear equations and their graphs. Students formalize their understanding of equivalent algebraic expressions and begin their study of polynomial expressions. Further, they learn that there are some actions that, when applied to the expressions on both sides of an equal sign, will not result in an equation with the same solution set as the original equation. Finally, they encounter problems that induce the full modeling cycle.
To access this resource, you will need to create a free account for the system on which it resides. The partner provides personalized features on their site such as bookmarking and highlighting which requires a user account.
This resource includes an introductory lesson on developing the law of exponents. A student created python coded program is used to develop the laws and there is also a two truths and a lie activity for application of the laws.

Students will find helpful resources for learning and practicing math skills and processes in this eMediaVA collection.

This collection has resources organized by grade level teachers can use to teach math.

Operations with expressions written in scientific notationMathematics Instructional Plans (MIPs) help teachers align instruction with the Mathematics Standards of Learning (SOL) by providing examples of how the knowledge, skills and processes found in the SOL and curriculum framework can be presented to students in the classroom.
Students are given 28 expressions with exponents that need to be simplified that cover multiple exponent rules. When simplified, there are 7 possible solutions.