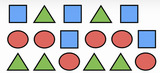
Unit 4 in Grade 4 introduces students to the more abstract geometric concepts of points, lines, line segments, rays, and angles. Students learn to measure angles and then use this skill to classify shapes based on their angle measure, a geometric property. Students also develop an understanding of reflectional symmetry, identifying line-symmetric shapes and drawing their lines of symmetry.
This unit builds on lots of work in prior grades with shape recognition and categorization (1.G.1, 2.G.1, 3.G.1). In order to differentiate a square from a rhombus, students must attend to the angle measure of the corners, or vertices. Thus, this unit introduces students to the vocabulary that will allow them to talk about angle measure as an attribute of plane figures (both polygons and more abstract figures, such as sets of intersecting lines), as well as the measurement system used to quantify angle measure precisely.
The unit begins with students drawing points, lines, line segments, rays, and angles, and continues to general classifications based on angles, including distinguishing between right, obtuse, acute, and straight angles as well as parallel, perpendicular, and intersecting lines. Then, students develop a more precise idea of angles as geometric figures that can be measured, and learn to do so. Students also learn to think of angles not just as objects but as actions—they can indicate a turn or change in direction. Students also see that angles are additive, just like other geometric measures they’ve explored in prior grades, such as length in Grade 2 (2.MD.1—6) and area in Grade 3 (3.MD.5—7). Next, students use their deepened understanding of angles to classify and draw triangles according to their angle measure (right, obtuse, and acute) as well as side length (equilateral, isosceles, and scalene) and quadrilaterals according to the parallel and/or perpendicular nature of their sides. Lastly, students explore lines of symmetry, finding and drawing them in figures.
This unit allows for particular focus on MP.2, MP.5 and MP.6. For example, when students are “shown two sets of shapes and asked where a new shape belongs,” they are reasoning abstractly and quantitatively (MP.2) (G Progression, p. 16). Students also learn to use a new tool, the protractor, precisely, ensuring they line up the vertex and base correctly and read the angle measure carefully (MP.5, MP.6).
This work continues to formalize much of the work students have already done in understanding geometric figures, which will continue to formalize in coming years. This unit prepares students to hierarchically classify two-dimensional figures in Grade 5 (5.G.3, 5.G.4). It also introduces students to drawing geometric figures, which they will see again in Grade 7 (7.G.1—3) and even high school Geometry and the trigonometric aspects of Algebra II. Thus, while all of the standards addressed in the unit are additional cluster standards, they lay an important foundation for geometric work in years to come.